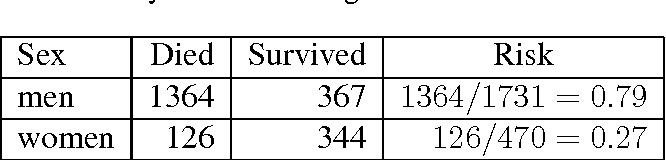
I just have a question regarding hazard ratios Are these similar to odds ratio? Re {MEDSTATS} relative risks, odds ratio, and hazard ratio in meta analysis RogerH 9/13/10 612 AM Or one could view the risk ratio and the odds ratio as approximations to the hazard ratio or rate ratio Rates and hazards can exceed 1, unlike risks, so there's no constraint on the hazard ratio, unlike the Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;
Q Tbn And9gcr Ttka12jaocnx Gn3ox9ci1ggq18vcw9359i6hq2cschyusam Usqp Cau
Cox regression hazard ratio and odds ratio
Cox regression hazard ratio and odds ratio-Odds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples of RR and OR for different probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 RR OR4 1 4 62 3 67 5804 01 4 03 67 66 Hazard ratio (HR) Broadly equivalent to relative risk (RR);An odds ratio greater than 1 indicates that the condition or event is more likely to occur in the first group And an odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the condition or event is less likely to occur in the first group The odds ratio must be nonnegative if it is defined It is undefined if p 2 q 1 equals zero, ie, if p 2 equals zero or q



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk
Intervals and statistical vs clinical significance This second article will discuss absolute and relative risks, number needed to treat and harm, KaplanMeier survival curves and understanding diagnostic tests What are absolute risks, relative risks, odds ratios and hazard ratios?Start studying Risk Ratio, Odds Ratio, KaplanMeier, Survival Analysis, Hazard Analysis Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools So, keep in mind that whenever we talk about the hazard ratio, relative risk, and odds ratio, there will always be a comparison to be made These values are dependent on another value for context Photo by Tingey Injury Law Firm on Relative risks all have a
Odds ratios work the same An odds ratio of 108 will give you an 8% increase in the odds at any value of X Likewise, the difference in the probability (or the odds) depends on the value of X So if you do decide to report the increase in probability at different values of X, you'll have to do it at low, medium, and high values of XA significant benefit was also observed with respect to the confirmed objective response rate and the time toHazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratio (E vs C) for the time period
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) In casecontrol studies, andLe Hazard Ratio (HR) est proche du RR avec une dimension temporelle supplémentaire En effet, dès lors que l'on est en présence de données censurées, c'estàdire des temps d'événement inconnus à causes de durées de suivi différentes selon les patients, le tableau de contingence précédent n'est plus valableThe hazard ratio would be 2, indicating higher hazard of death from the treatment Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratios suffer somewhat less from selection bias withJul



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value
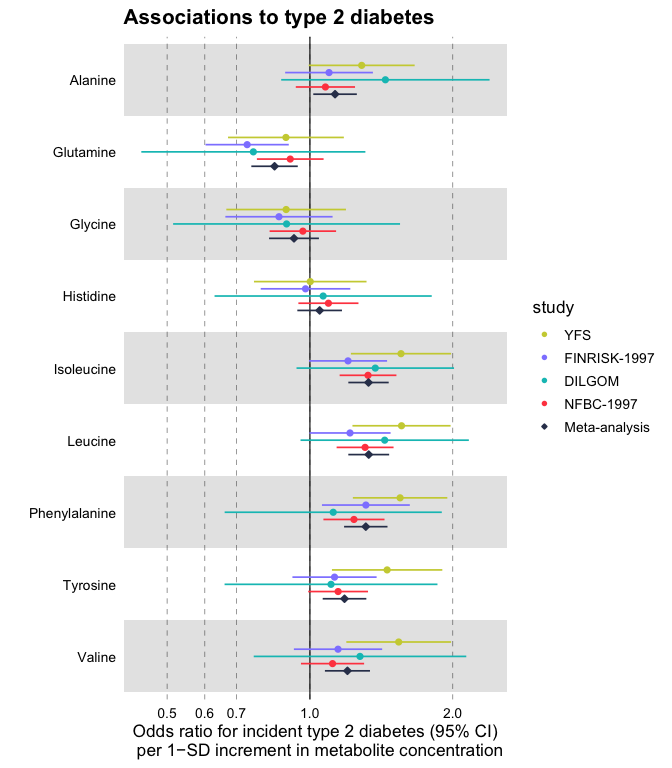



Forestplots Of Measures Of Effects And Their Confidence Intervals Ggforestplot
The ratio of the odds for female to the odds for male is (32/77)/(17/74) = (32*74)/(77*17) = 1809 So the odds for males are 17 to 74, the odds for females are 32 to 77, and the odds for female are about 81% higher than the odds for males Now we can relate the odds for males and females and the output from the logistic regressionThe odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of an event or disease occurring in one group to the odds occurring in another group The standard formula is X / ( 1 − X) / Y / ( 1 − Y), where X and Y are the probability of that event in the two groups, respectively In contrast, the relative risk is the risk of an event or diseaseThe odds ratio (OR) is a measure of how strongly an event is associated with exposure The odds ratio is a ratio of two sets of odds the odds of the event occurring in an exposed group versus the odds of the event occurring in a nonexposed group Odds ratios commonly are used to report casecontrol studies The odds ratio helps identify how likely an exposure is to lead to a specific




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar
And the statistic given was "hazard ratio 0 (95% CI , p value=0013) In every other way the hazard ratio is similar to odds ratio and relative risk wherein treatment efficacy is denoted by a hazard ratio of less than 10 in prevention trials and a hazard ratio of more than 10 in treatment trials Table 3 Hazard ratio and timetoevent analysis 1 Hazard ratio (E vs C) for the time period Please note that results shown are rounded to 2 decimal places, but the calculations used the raw numbers from the previous column ( c ) and therefore give different results than if the rounded numbers were used (eg, 006/008 = 075)




Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad




Hazard Ratio Wikipedia
RealRisk works with any study which investigates the link between a risk factor or intervention and an outcome of interest, which also reports one of the following a relative risk (RR), hazard ratio (HR), odds ratio (OR) or a percentage change The study can be observational or experimental in design The terminology used can vary – so don't be put off if the terms 'risk factor' and Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a1 Log hazard ratio of dropout from the maintenance treatment program between patients in clinics B and A who take 50mg dose of methadone 2 Log hazard ratio of dropout from the maintenance treatment program between two individuals who are at clinic A and whose dosage differs by 1 mg 3 Difference in log hazard ratio of dropout from the




Figure 2 From Events Per Person Time Incidence Rate A Misleading Statistic Semantic Scholar



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
In logistic regression, an odds ratio of 2 means that the event is 2 time more probable given a oneunit increase in the predictor In Cox regression, a hazard ratio of 2 means the event will occur twice as often at each time point given a oneunit increase in the predictor Are these not practically the same thing? The odds ratio is the measure of choice in a casecontrol study (see Lesson 1) A casecontrol study is based on enrolling a group of persons with disease ("casepatients") and a comparable group without disease ("controls") The number of persons in the control group is usually decided by the investigator95% confidence interval, 025 to 047;




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



Plos One Pcsk9 Loss Of Function Variants And Risk Of Infection And Sepsis In The Reasons For Geographic And Racial Differences In Stroke Regards Cohort
The hazard ratio would be 2, indicating higher hazard of death from the treatment Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereofHazard ratio for progression or death, 034;The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions
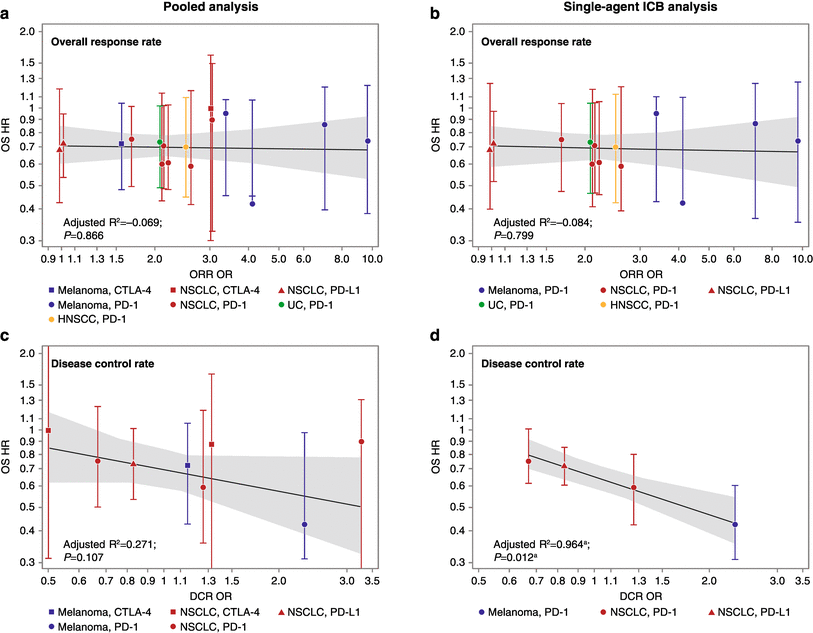



Figure 6 Evaluation Of Classical Clinical Endpoints As Surrogates For Overall Survival In Patients Treated With Immune Checkpoint Blockers A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Springerlink



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsIt is called that because it is the ratio of two odds Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio That is fine English, but this can quickly lead to confusion If you did that, you would have to call this calculation the odds ratio ratio or the ratio of the odds ratiosFor instance, a disease free survival was longer for an anastrozole group compared to a tamoxifen group;




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy
Furthermore, the odds ratio of 258 for all persons is not a weighted average of the odds ratios of 265 for men and 291 for women, as 258 is closer to 1 than either stratumspecific estimate Adjusting the odds ratio of 258 for sex, using MantelHaenszel methods, produces an odds ratio of 279, though sex is not a confounderP less than 0001);Odds ratio the ratio of cross products This is not true for relative risk Switching the rows or columns inverts the odds ratio For example, the odds ratio for no cough given a history of bronchitis = (247/26)/(1002/44) = 0417 = 1/2397 This is the reciprocal of the OR for cough




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programRather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notThe method of presenting the results of clinical studies can



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Outcomes Shown For A Odds Ratio Analysis And B Hazard Ratio Download Scientific Diagram
Useful when the risk is not constant with respect to time It uses information collected at different times TheHazard ratio, odds, and probability of healing There is an alternative interpretation of the hazard ratio that may be intuitively easier to understand The hazard ratio is equivalent to the odds that an individual in the group with the higher hazard reaches the endpoint first Thus, in a clinical trial examining time to disease resolution, itIn a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;




Clinical Trials In Hours Point Estimation Odds




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
The odds ratio is simply the ratio between the following two ratios The ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who died, and the ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who survived From the data in the table 1, it is calculated as follows OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (152/17)/More on the Odds Ratio Ranges from 0 to infinity Tends to be skewed (ie not symmetric) "protective" odds ratios range from 0 to 1 "increased risk" odds ratios range from 1 to Example "Women are at 144 times the risk/chance of men" "Men are2 days ago In odds ratio, we take ratio of those odds in two different groups Step 1 At first, we calculate the odds in those comparison groups Cases Odds that a case was exposed = Probability of exposures in cases / Probability of nonexposures in cases = Number of exposed among cases (a) / total number of cases (ac) / Number of not exposed among
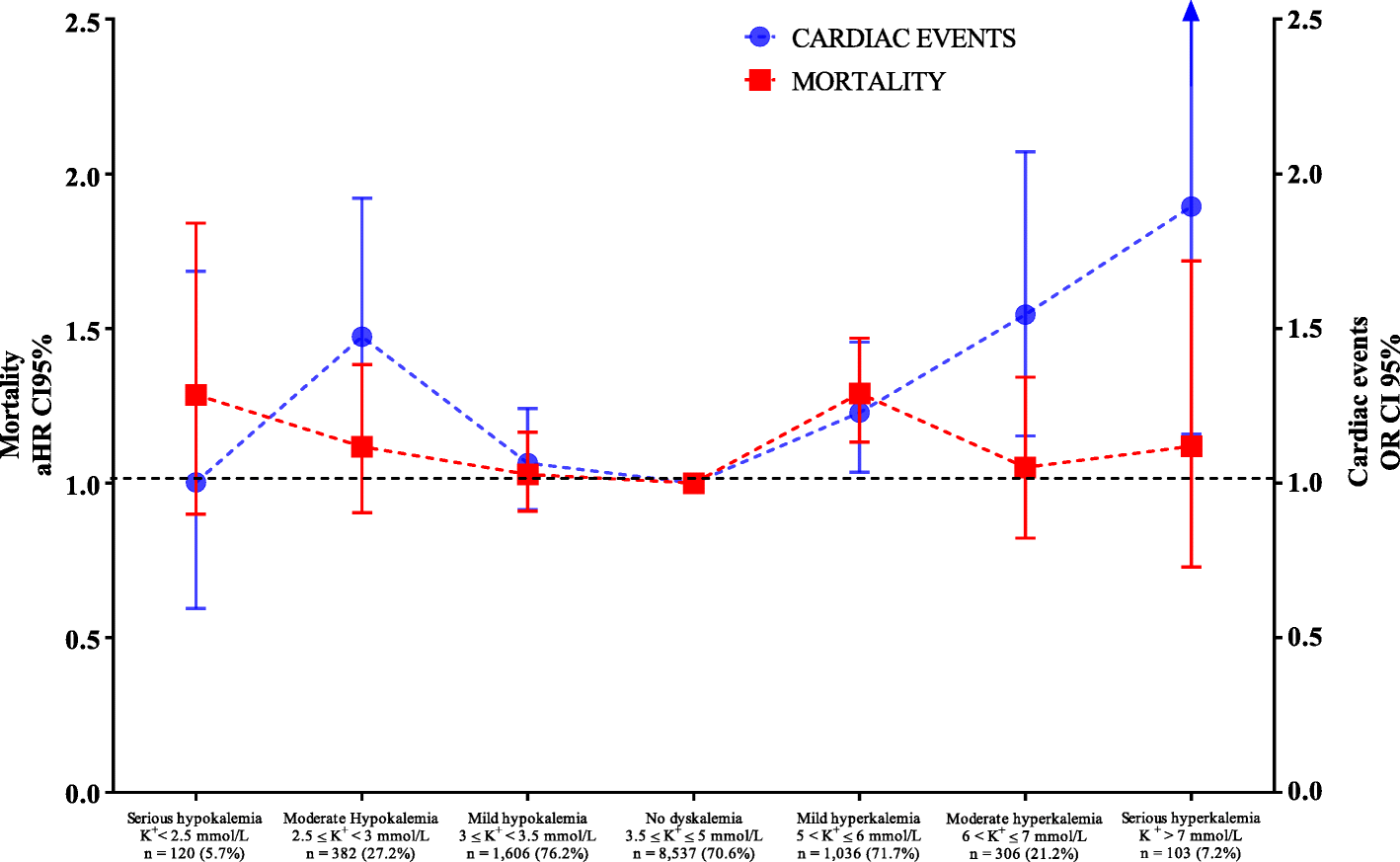



Influence Of Dyskalemia At Admission And Early Dyskalemia Correction On Survival And Cardiac Events Of Critically Ill Patients Critical Care Full Text



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
This is called the odds ratio;Cox regression vs logistic regression Distinction between hazard/rate ratio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precision The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either of



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
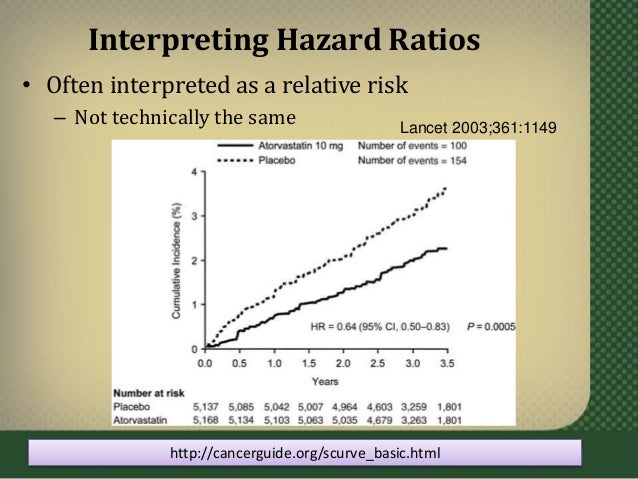
Tyring, S, R A Barbarash, J E Nahlik, A Cunningham, J Marley, M Heng, T Jones, T Rea, R Boon, R Saltzman, and Collaborative Famciclovir Herpes ZosterThe odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RR




Approximate Reciprocal Relationship Between Two Cause Specific Hazard Ratios In Covid 19 Data With Mutually Exclusive Events Medrxiv




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators Let's say that in your experiment the calculated Hazard Ratio is equal to 065 This is how you can interpret and report it The mortality rate in a group of smokers drops by 35% compared to the group of highcalorie diet The mortality rate among smokers is 065 times of that among patients with a highcalorie diet



Hazard Ratios
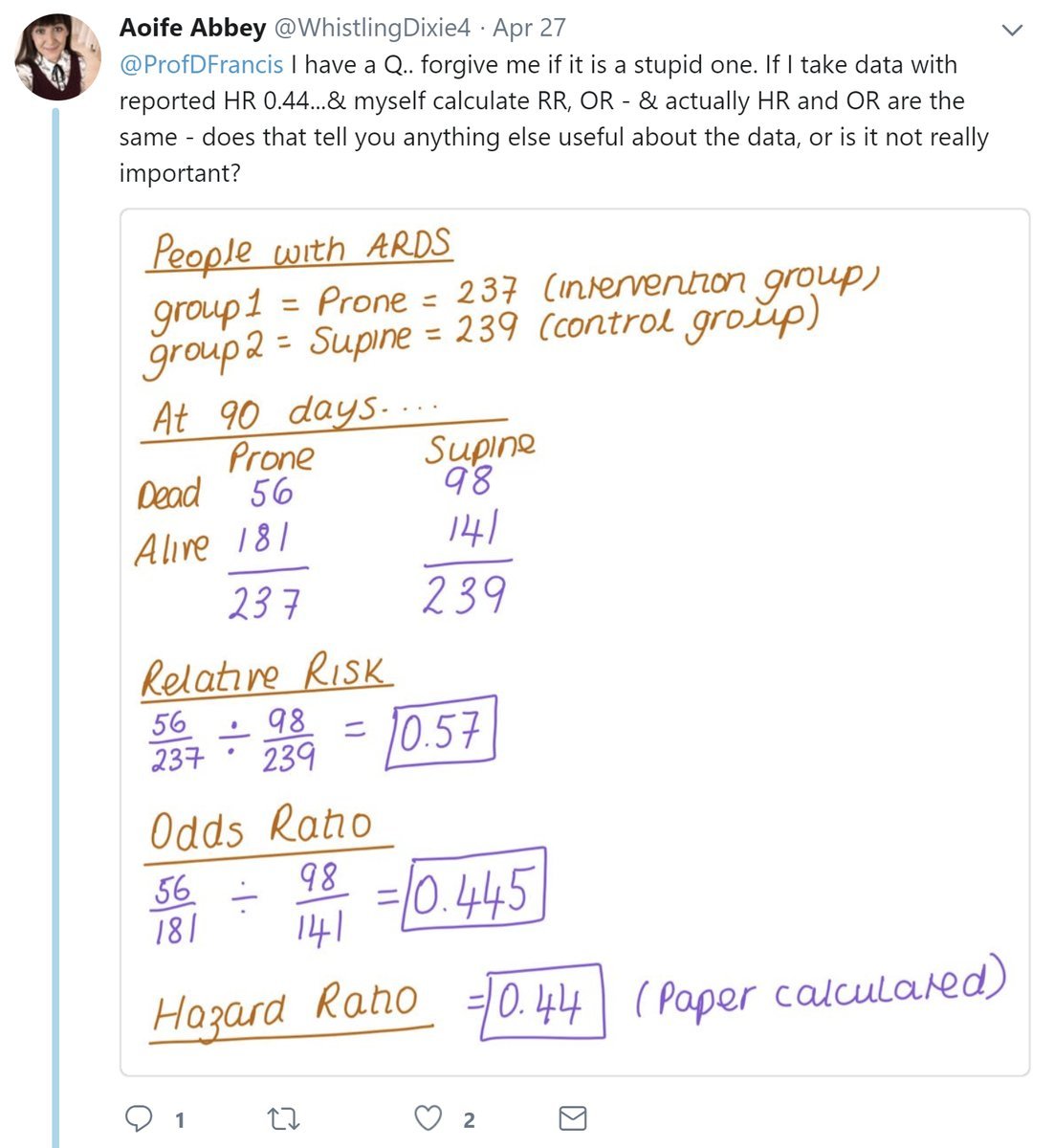



Prof Darrel Francis Mk Cardiofellows Great Again The Hazard Ratio Is In A Way The Best Thing We Could Calculate Because It Looks Along Every Instant In Time And
In cohort A, imagingbased progressionfree survival was significantly longer in the olaparib group than in the control group (median, 74 months vs 36 months; Reviewed and revised 26 August 15 OVERVIEW An odds ratio (OR) is a measure of association between an exposure and an outcome The OR represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposure




Hazard And Odds Ratios Image Eurekalert Science News




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp




Various Estimates For The Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Of Herpes Download Table
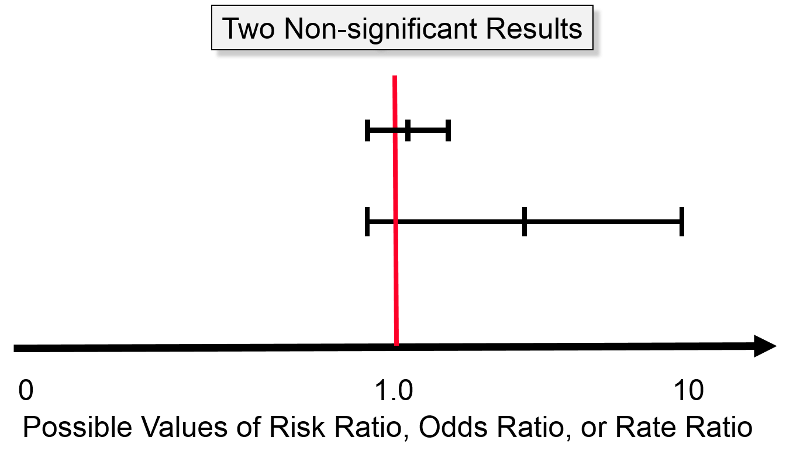



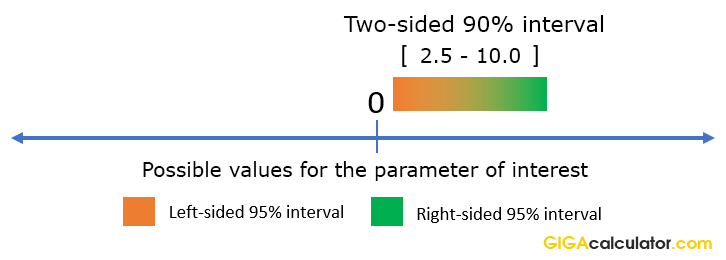
Confidence Intervals And P Values




Thread By Profdfrancis Risk Ratio Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio 2nd And Final Part Of The Tweetorial From Orbita Hq Fun Easy And Informativ Meded Foamed Cardiology Cardiotwitter




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow
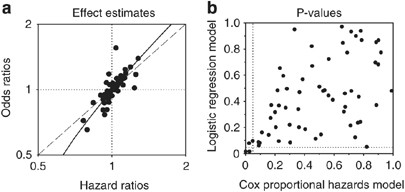



Cox Proportional Hazards Models Have More Statistical Power Than Logistic Regression Models In Cross Sectional Genetic Association Studies European Journal Of Human Genetics



Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio
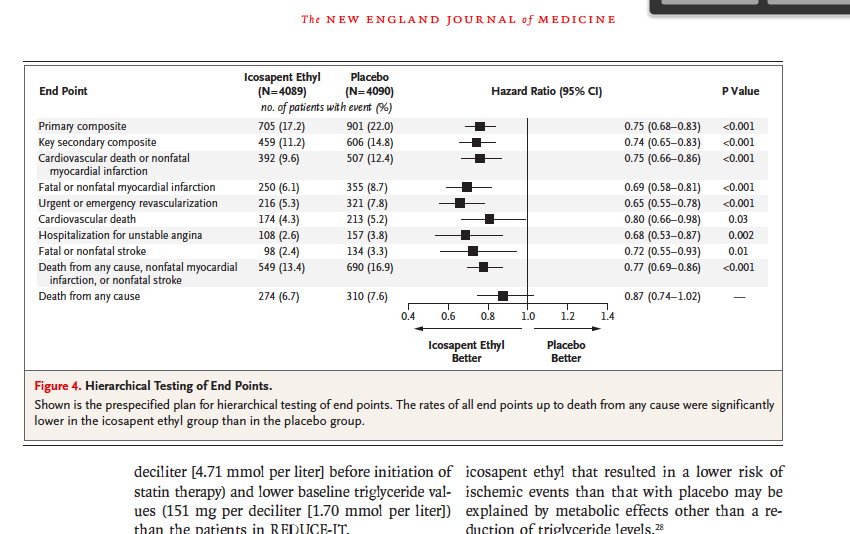



State The Mean Median Hr Hazard Ratio Chegg Com




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Introduction To Cox Regression Kristin Sainani Ph D



How To Remember The Differences Between Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Likelihood Ratio And In What Instances They Should Be Applied Quora




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Q Tbn And9gcqsrft9mxr7dpz7nmjrd2rigdx Ivp6aahq2v9iti13quuix7yw Usqp Cau




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Biostatistics Primer What A Clinician Ought To Know Hazard Ratios Sciencedirect




Hazard Ratios




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Odd Ratio Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Approximate Reciprocal Relationship Between Two Cause Specific Hazard Ratios In Covid 19 Data With Mutually Exclusive Events Medrxiv




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
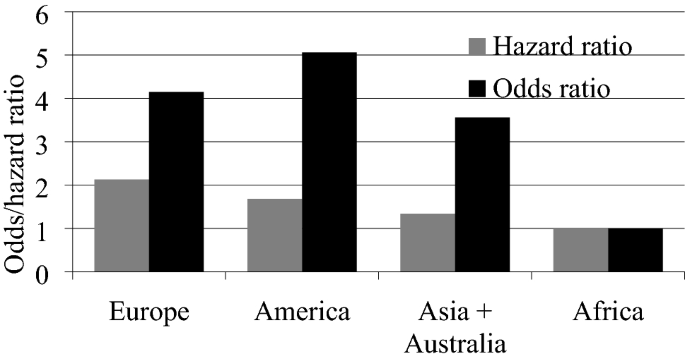



A Survival Analysis In The Assessment Of The Influence Of The Sars Cov 2 Pandemic On The Probability And Intensity Of Decline In The Value Of Stock Indices Springerlink
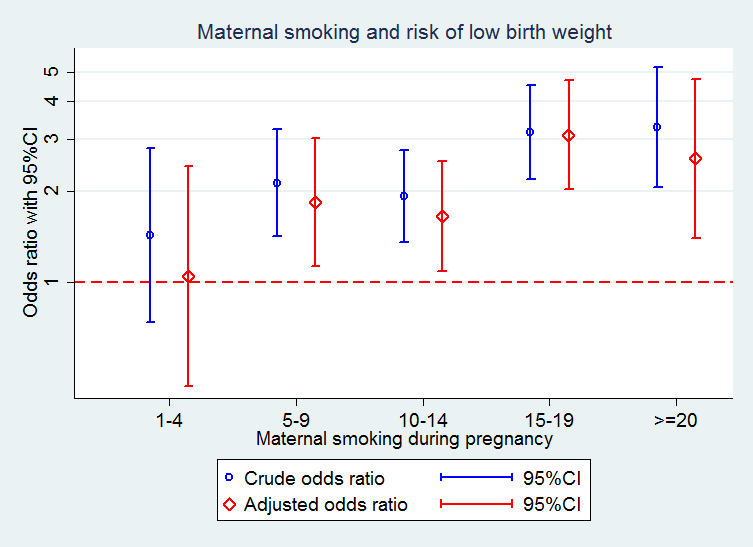



Medical Statistics And Data Science Statistics



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Www Goldjournal Net Article S0090 4295 18 8 Pdf



2




Hazard Ratios For Progression Free And Overall Survival And Odds Ratios Download Scientific Diagram




Abc Transporter Genes And Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes Care




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Forest Plots Of Hazard Ratios Hrs For Overall Survival A And Odds Download Scientific Diagram




Calculating The Risk Ratio Odds Ratio And Risk Difference In A Randomised Controlled Trial Youtube
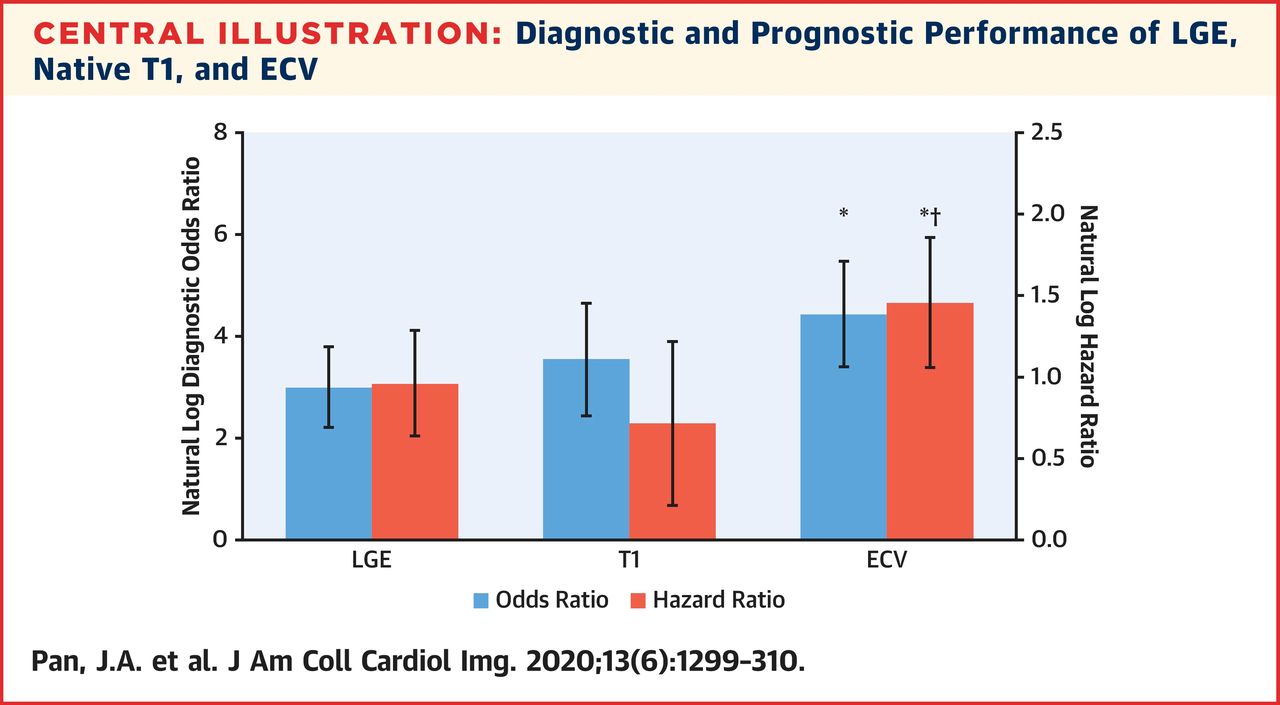



Jacc Journals Jaccimg Explores Cmr In Cardiac Amyloidosis T1 Mapping Has Similar Sensitivity Specificity While Avoiding Contrast Ecv Has Highest Diagnostic Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio For Adverse Events
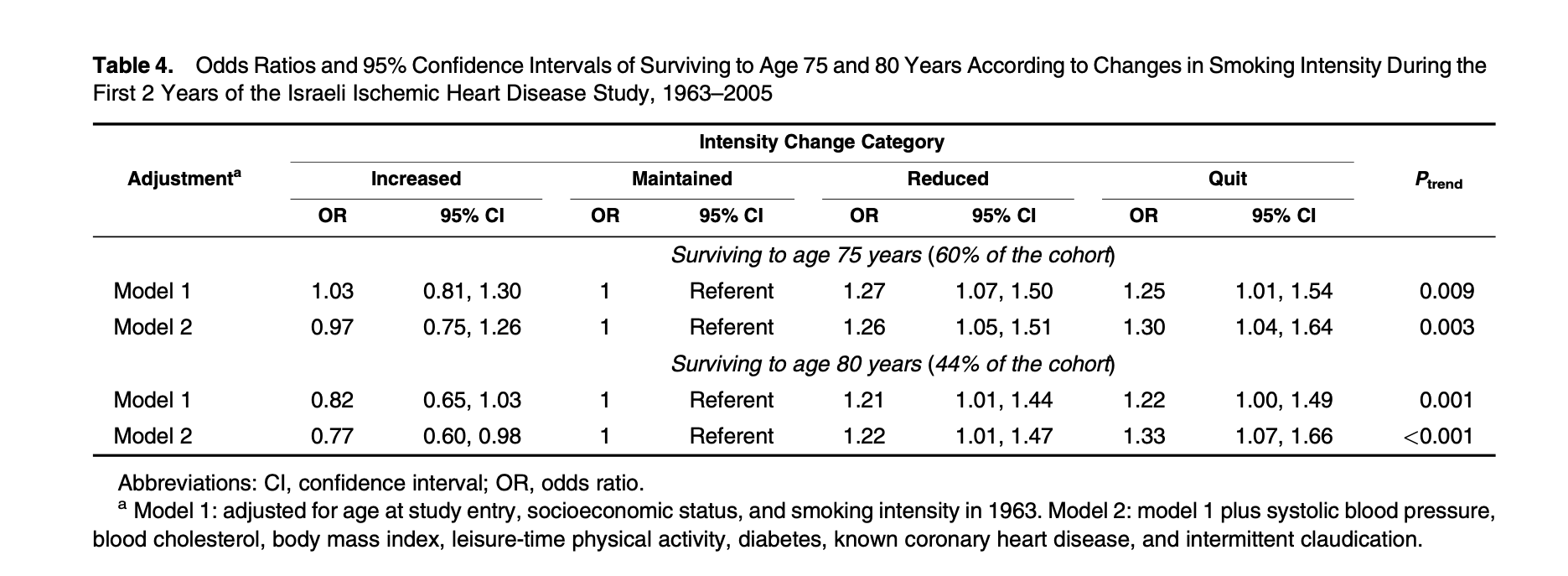



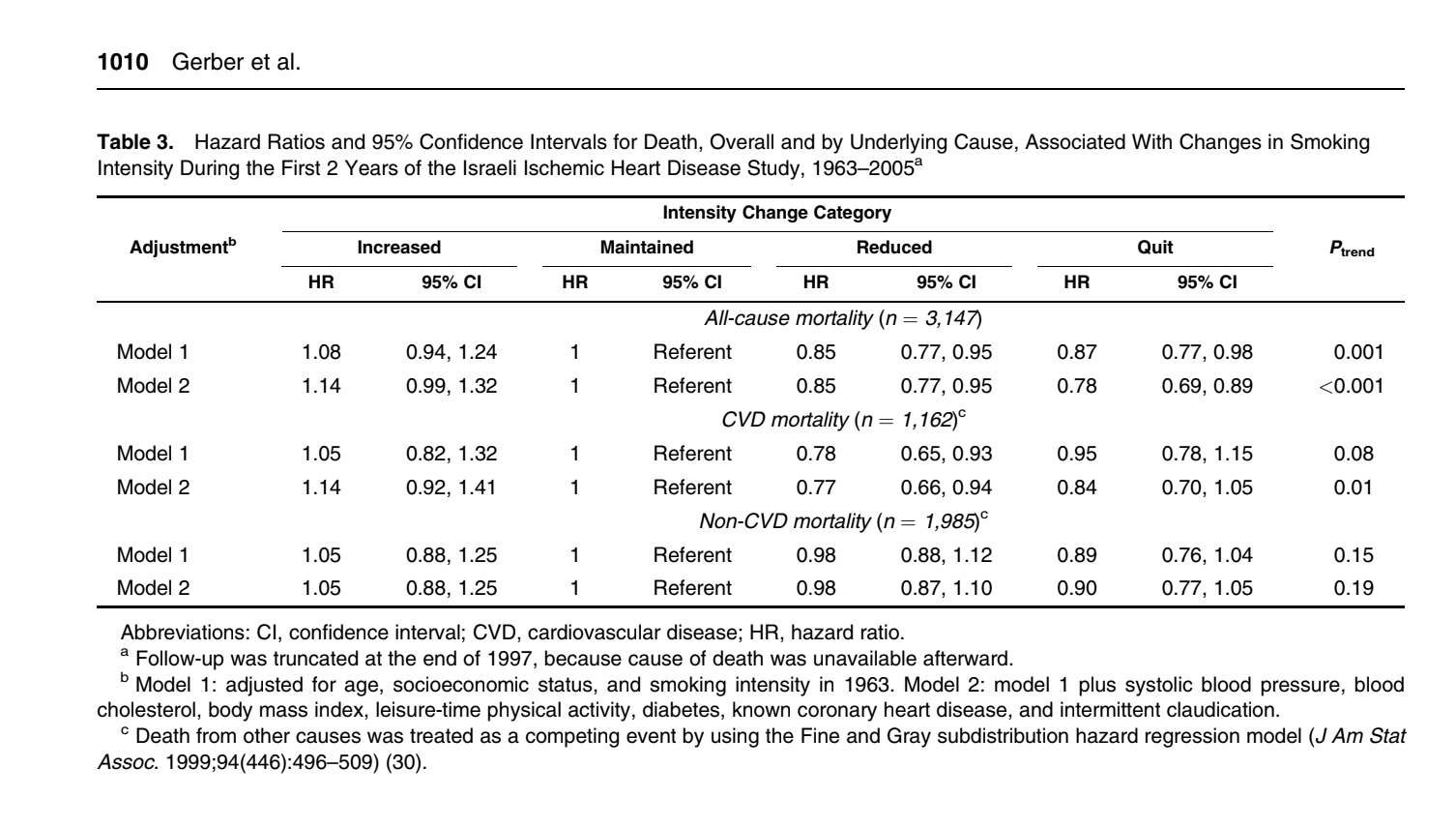
Solved Table 3 Provides Hazards Ratios 1 For The Reduce Chegg Com
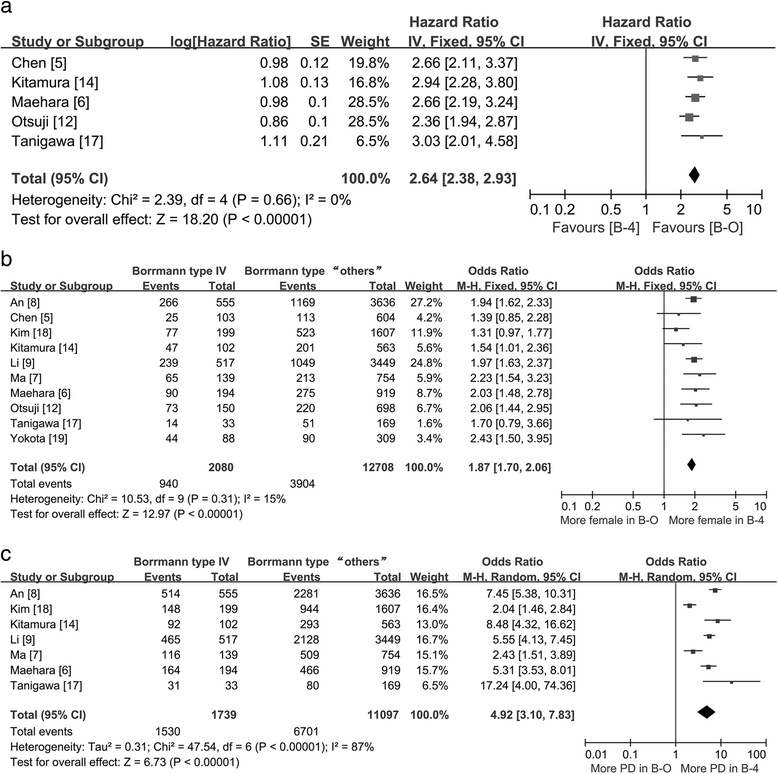



Clinicopathologic Characteristics And Prognosis Of Borrmann Type Iv Gastric Cancer A Meta Analysis World Journal Of Surgical Oncology Full Text




Fillable Online Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Fax Email Print Pdffiller
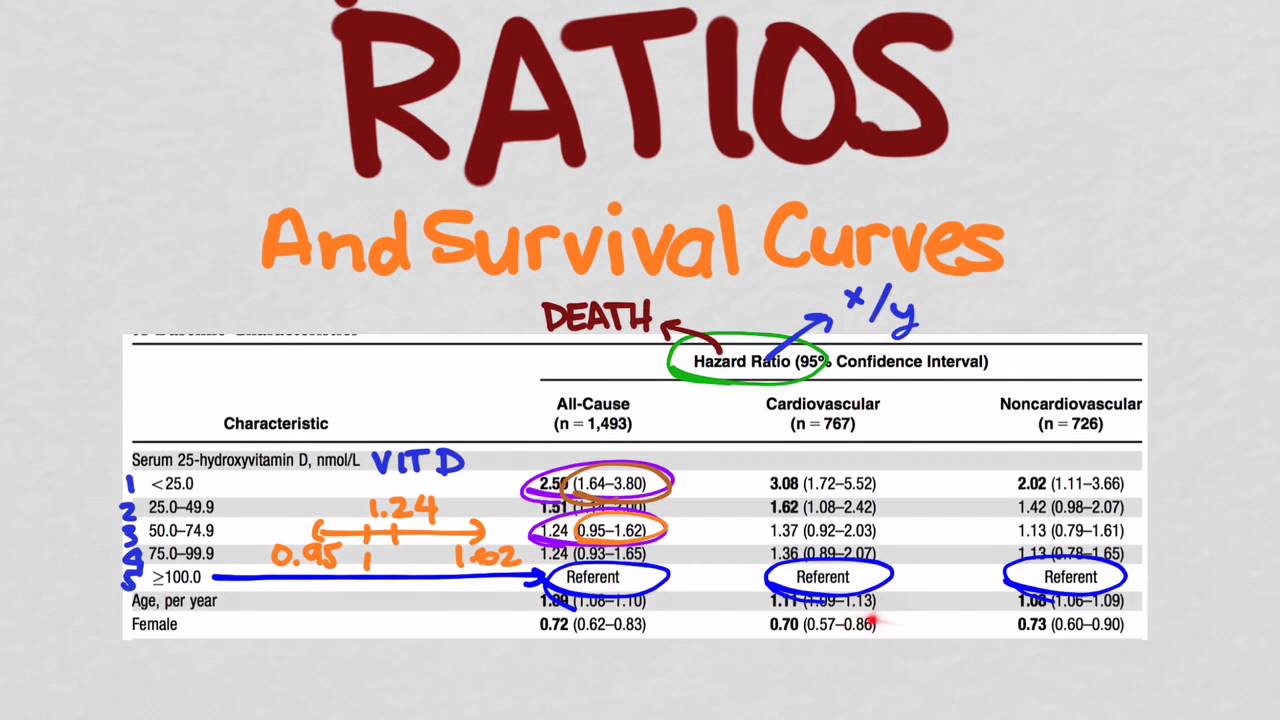



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube




Measures Of Association Ppt Download




The Utility Of Mortality Hazard Rates In Population Analyses Biorxiv



Q Tbn And9gcr Ttka12jaocnx Gn3ox9ci1ggq18vcw9359i6hq2cschyusam Usqp Cau




Odds Ratio And Hazard Ratio For Complications Download Table
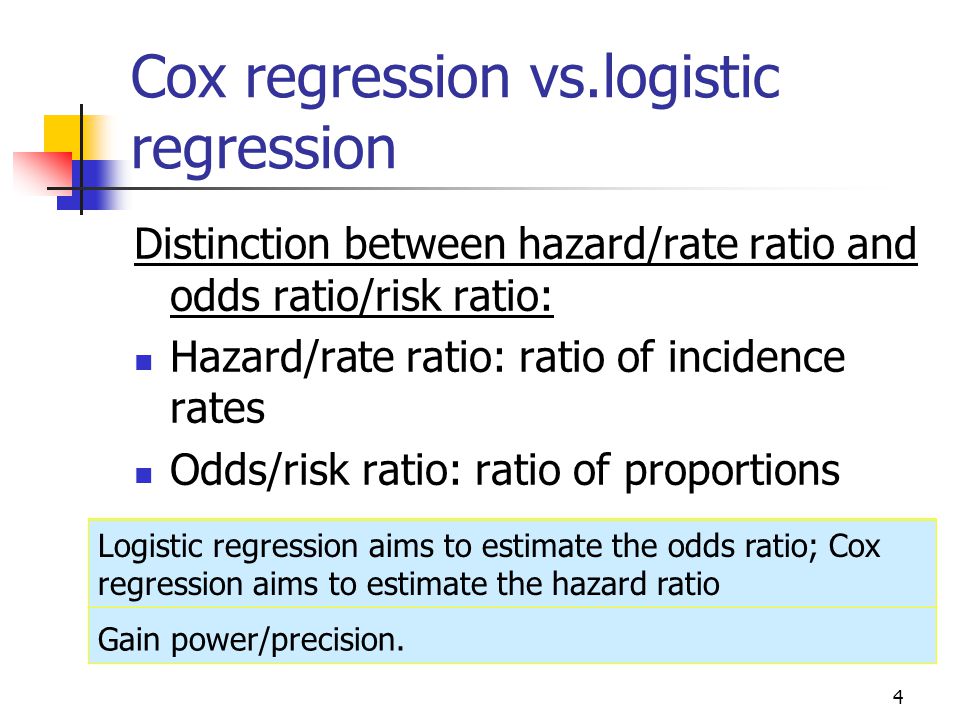



Statistics 262 Intermediate Biostatistics Ppt Video Online Download




Ctspedia Ctspedia Clinaegraph001
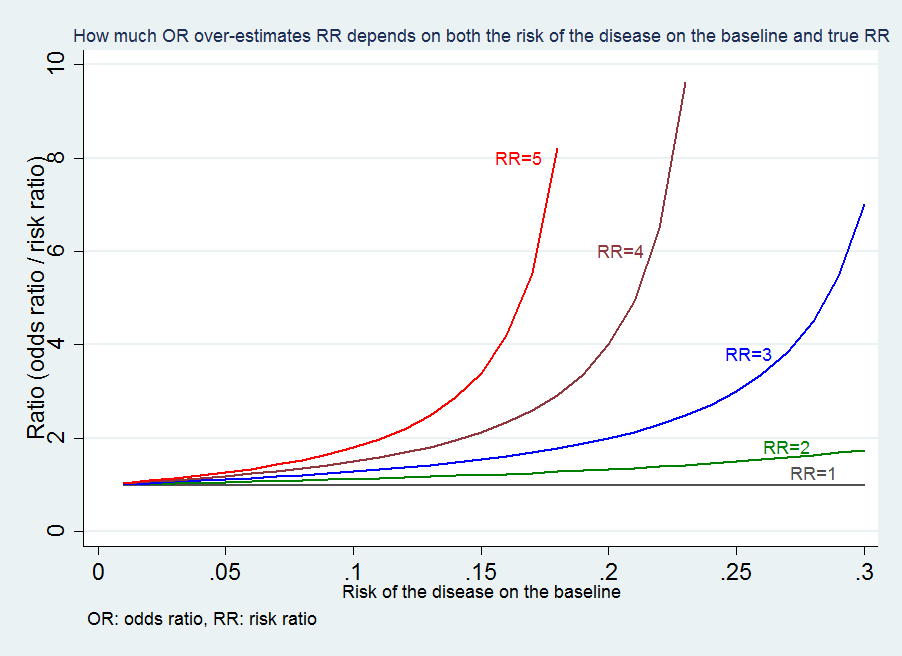



Medical Statistics And Data Science Statistics




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Kaplanmeier Methods And Parametric Regression Methods Kristin Sainani




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube



Plos One Hospital Admission With Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Associated With Increased All Cause Mortality Independent Of Cardiovascular Risk Factors



Solved Table 3 Provides Hazards Ratios 1 For The Reduce Chegg Com




Jci Insight Plasma Copeptin And Chronic Kidney Disease Risk In 3 European Cohorts From The General Population




Introduction To Biostatistics For Clinical And Translational Researchers




Uuqnbke2fl8epm




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Stat D Si Relative Risk Pdf4pro




Lincom Stata




Design And Analysis Of Clinical Study Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Dr Tuan V Nguyen Garvan Institute Of Medical Research Sydney Australia Ppt Download




Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio




Study Mortality With Hazard Rates Not Probabilities Biorxiv



Http Aspirekpco Weebly Com Uploads 1 5 9 3 Session 6 Statistical Interpretation 19 Pdf




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



1




Pierfilippo De Sanctis Pfdesanctis Profile Pinterest



Http Journal Emwa Org Observational Studies Odd Cases And Risky Cohorts Measures Of Risk And Association In Observational Studies Article 3240 Mew 263 Lang Pdf




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True




Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿